Women have significantly impacted the technology industry for many years, and this trend continues to grow. From product development to company culture, women have played a crucial role in shaping the tech industry in many positive ways. In this blog post, we will discuss the impact that women have had on technology and why it is essential to have balanced leadership in organizations between men and women to maximize productivity.
Current Statistics of Women in Tech
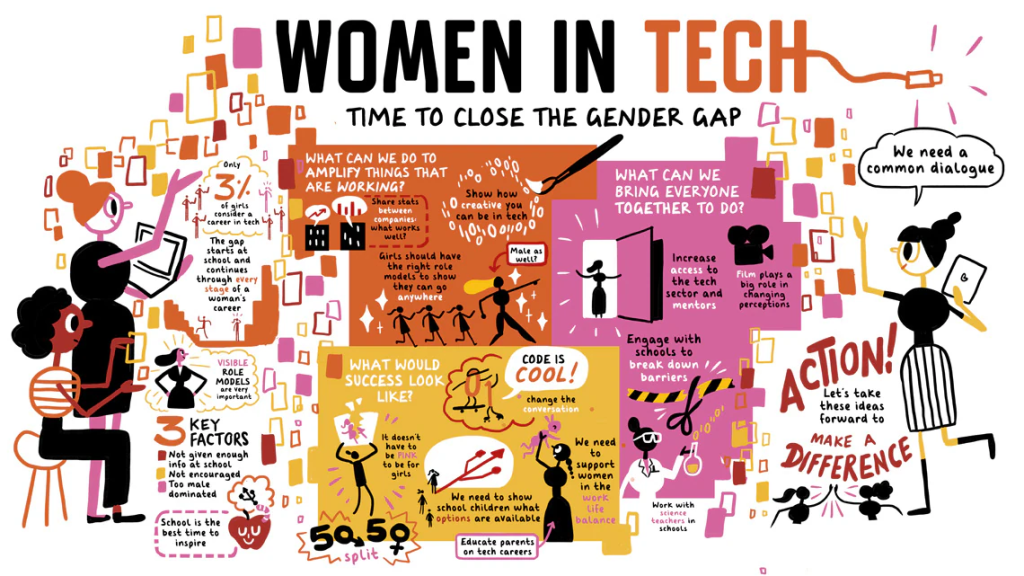
Despite the progress that has been made, there is still a significant gender imbalance in the tech industry. According to recent statistics, women make up just 25% of the tech workforce globally. This imbalance is even more pronounced in leadership positions, where women hold just 11% of CEO positions in tech companies.
Diverse Perspectives and Problem-Solving Approaches
Women bring unique perspectives and problem-solving approaches to the technology industry, which can lead to more innovative and user-centred products and services. For example, the development of maternal and child health technologies, education technologies, and financial services for women has been largely driven by women’s needs and experiences. As a result, these products and services have been designed with a better understanding of the user’s needs, leading to higher user satisfaction.
Bridging the Gender Gap in the Tech Industry
Women in technology have been advocating for greater representation and equal opportunities for women in the industry. This has helped to increase awareness of the gender gap and drive change towards more diverse and inclusive workplaces. The presence of women in leadership positions has also helped to create a more welcoming and supportive environment for women in the industry.
Positive Influence on Company Culture
Research has shown that having more women in leadership positions can have a positive impact on company culture, leading to increased collaboration and more ethical decision-making. Companies with more gender diversity in their leadership teams have been found to be more innovative and better equipped to tackle complex problems. This is because a diversity of perspectives and experiences leads to more creative and effective solutions.

Inspiring Girls to Pursue Careers in STEM
The presence of women in technology can serve as role models and inspire girls to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) fields. This is particularly important as the tech industry is one of the fastest-growing industries in the world and will continue to play a critical role in shaping our future. Encouraging girls to pursue careers in STEM fields helps to ensure that future generations of women will have equal representation and opportunities in the tech industry.
The Importance of Balancing Leadership in Organizations
A balanced leadership between men and women in organizations is essential to maximize productivity. Companies with gender-diverse leadership teams tend to be more innovative, better equipped to tackle complex problems, and have a positive influence on company culture. This is because a diversity of perspectives and experiences leads to more creative and effective solutions.

Improving Representation of Women in Tech
To improve the representation of women in the tech industry, it is essential to take a multi-faceted approach. This includes creating a welcoming and supportive work environment, offering equal opportunities and flexible work arrangements, and providing mentorship and leadership programs for women in the industry. Additionally, organizations must also work to increase the number of girls and women pursuing careers in STEM fields by offering STEM education programs and providing mentorship and support for young women in the industry.
In conclusion, women have made a significant impact on the technology industry, and their presence continues to shape the industry in many positive ways. From product development to company culture, women have played a crucial role in advancing the tech industry. It is essential to have balanced leadership between men and women in organizations to maximize productivity and drive innovation. However, there is still a significant gender imbalance in the tech industry, and more needs to be done to improve the representation of women in the field. Organizations can take steps to create a welcoming and supportive work environment, offer equal opportunities and flexible work arrangements, and invest in mentorship and leadership programs for women. Additionally, encouraging girls and young women to pursue careers in STEM fields is essential for future generations of women to have equal representation and opportunities in the tech industry. Overall, the positive impact of women in technology cannot be overstated, and it is important for organizations to work towards a more diverse and inclusive tech industry.











